Melanoma and the Importance of Prevention and Screening
Melanoma, while less common than other skin cancers, is the most dangerous and potentially life-threatening form of skin cancer.
Medically reviewed and written by Dr Kok Wai Leong
22 May 2025
Share
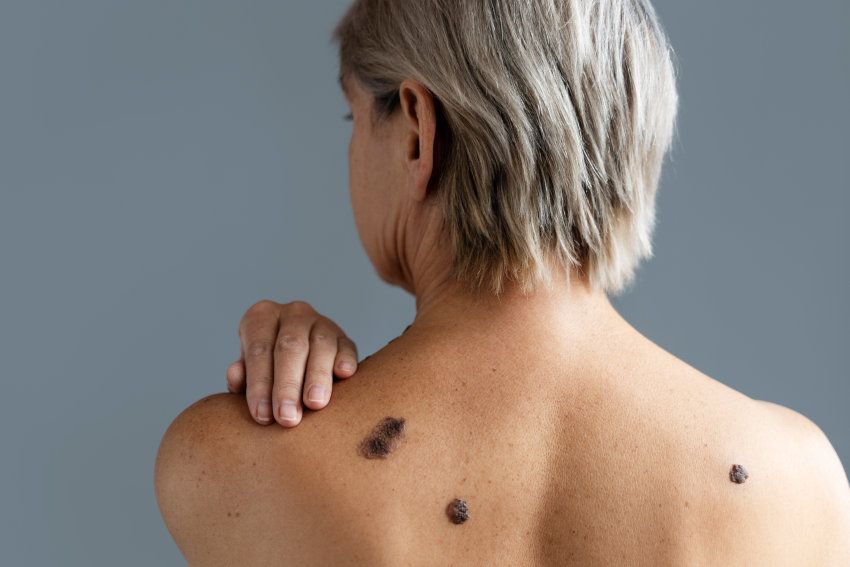
Melanoma, while less common than other skin cancers, is the most dangerous and potentially life-threatening form of skin cancer. In Singapore, our tropical weather brings along year-round sunshine, and the skin damage caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a very important risk factor for the development of melanoma.
It is necessary to highlight that melanoma can be preventable and early detection will allow early treatment. Therefore, it is important to understand how melanoma develops, how to spot it, and why regular screenings with a dermatologist should be scheduled.
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that originates in the melanocytes, which are cells responsible for producing pigment that gives skin its color. It typically develops in the skin, but can also occur in the eyes or other mucous membranes. While rarer, melanoma is the most concerning due to its aggressive nature. It is a dangerous form of skin cancer because of its ability to spread to other parts of the body.
The majority of melanomas are linked to excessive UV exposure, whether from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. This exposure damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that result in uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells.
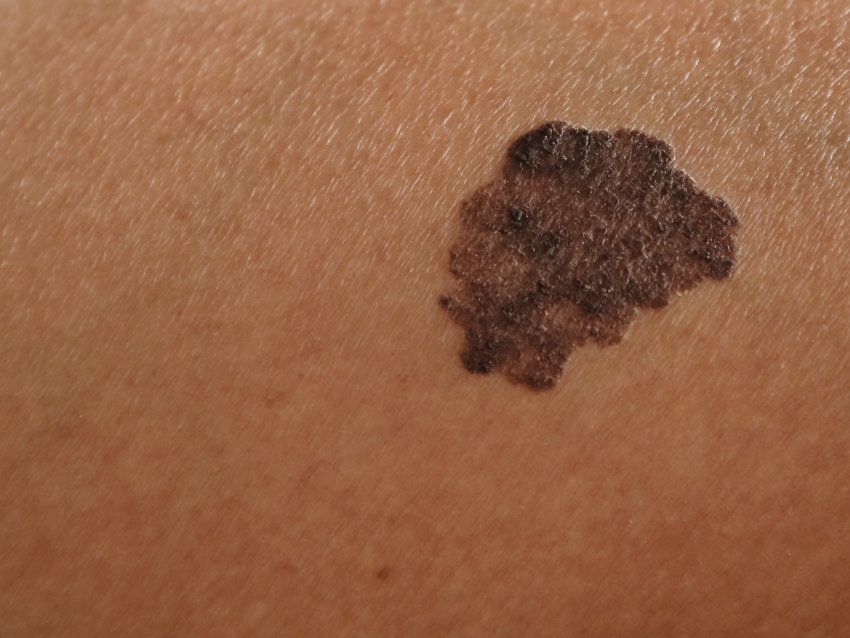
Who is at risk?
While anyone can develop melanoma, some people are at higher risk than others. Risk factors include:
- A history of excessive sun exposure or sunburns
- Fair skin, freckling, or red/blonde hair
- A family history of melanoma or other skin cancers
- The presence of many moles or atypical (irregular) moles
- A weakened immune system
Singaporeans have a diverse population and different skin tones. While people with lighter skin are more prone to sunburns and UV damage, individuals with darker skin tones are not immune to skin cancer. In fact, melanoma can sometimes be more difficult to detect in darker skin due to the color of the lesions.
Warning Signs of Melanoma
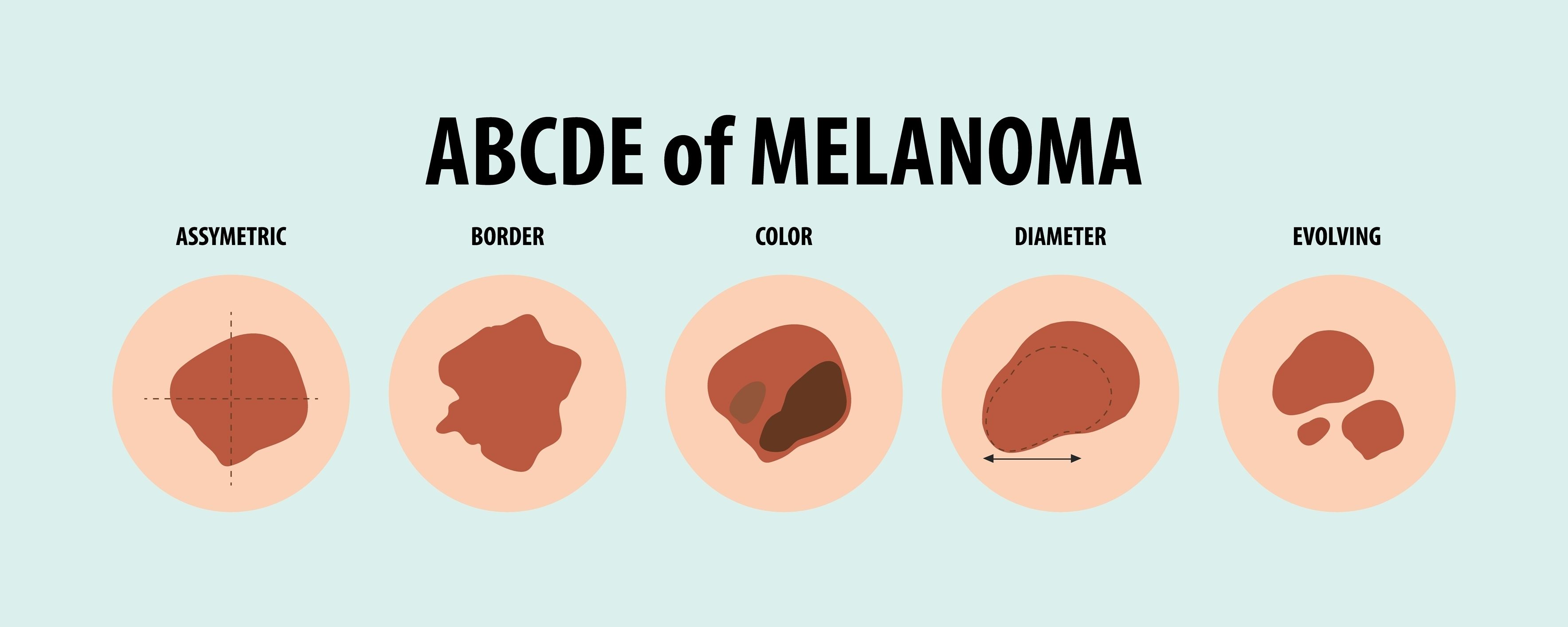
Melanoma can develop from existing pigmented spots like moles, or appear as a new growth on the skin. We use an easy to remember mnemonic, the ABCDE rule, a helpful guide for spotting early signs on the skin:
- A for Asymmetry: If one half of the mole looks different from the other, it may be a sign of melanoma.
- B for Border: Melanomas often have irregular or blurred borders.
- C for Color: A variety of colours (black, brown, red, white, blue) within a mole can signal melanoma.
- D for Diameter: Moles larger than 6 millimetres are at higher risk as well.
- E for Evolving: Changes in a mole’s appearance, such as its size, shape, color, or elevation, with time, should warrant an early review.
It is advisable that if you notice any of these warning signs to schedule a dermatologist review as soon as possible.
Skin Screenings are Important
Because melanoma can develop in even seemingly healthy skin, regular skin exams with a dermatologist can help identify early signs of the disease before it spreads. Dermatologists are trained to spot suspicious moles or lesions that may not be noticeable to the untrained eye, and they have the tools and expertise to diagnose melanoma accurately.
During a routine skin screening, the dermatologist will carefully examine your skin from head to toe, including areas that are often overlooked, like between your toes, the scalp, and underarms. If they find any suspicious spots, they may take a biopsy—a small sample of tissue—to be tested for cancerous cells.
The earlier melanoma is detected, the easier it is to treat, and the better the chances for a full recovery. Unfortunately, once melanoma spreads to other parts of the body, it becomes much more difficult to treat effectively. This is why regular screenings with a dermatologist are so essential, especially for individuals at higher risk.
How Melanoma Can Be Prevented
While regular screenings are critical for early detection, prevention is equally important. Simple ways you can modify your daily activities to reduce the risks include:
- Limit Sun Exposure: The sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays lead to damage on the skin. Therefore, avoid prolonged sun exposure during peak hours (11 a.m. to 3 p.m.).
- Use Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every day, even when it’s cloudy or winter. Reapply every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Clothing that have UPF 30, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses can offer additional protection from the sun’s harmful rays.
- Be Mindful of Medications and Conditions: Certain medications, like antibiotics or oral contraceptives, can increase sun sensitivity. Additionally, conditions like a weakened immune system may also increase melanoma risk. Always discuss potential risks with your healthcare provider.
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer, yet we can take steps to prevent and detect it early. Good sun-safety habits, regular self-checks and annual skin check examinations with a dermatologist, can reduce your risk of development of melanoma.
If you suspect you have melanoma, schedule an appointment with Dr Kok, our Dermatologist here.

Dr Kok Wai Leong is an accredited dermatologist with a special interest in eczema, psoriasis, photodermatology and skin cancers.



